scloop: an embedding suite for single-cell Hi-C data
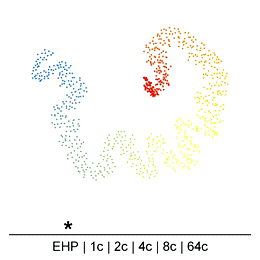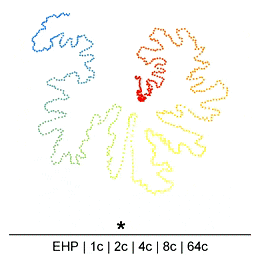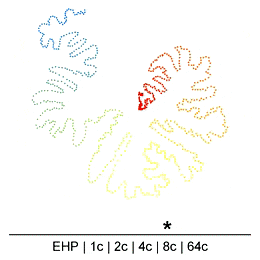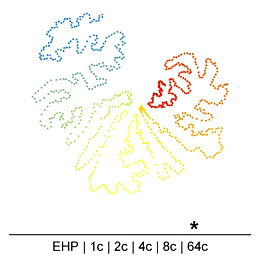
Chromatin in the Mammalian genome organized hierarchically at different scales which can be detected by Hi-C experiments at different resolutions. However, the existence or extent of chromatin structure variability across single cells remains debated. Many efforts have been made recently to develop different single-cell Hi-C (scHi-C) protocols and analysis tools to improve data yield and cell state identification accuracy, but the path towards a reliable and mature analysis pipeline remains unclear. Embedding is a critical step in single-cell analyses to capture population-or cell state-specific genomic features. Unsupervised embedding of scHi-C data is particularly challenging due to high dimensionality, extreme data sparsity, and cell-to-cell variations at different genomic scales. It is unclear if cell-to-cell variations are present at each scale of genome organization (e.g compartments, domains, loops) and whether existing embedding tools are viable for different biological questions (e.g., cell cycle dynamics, complex tissues, etc.), or under variable technical settings (sequencing depth, resolution, etc.).
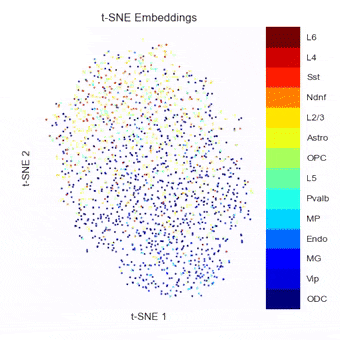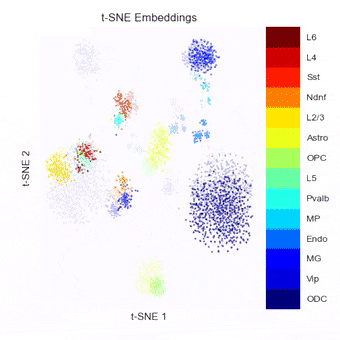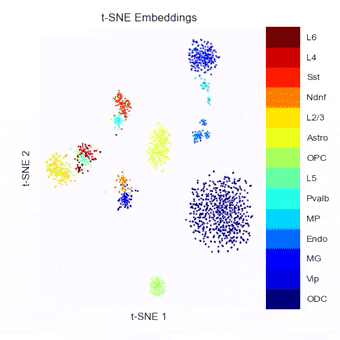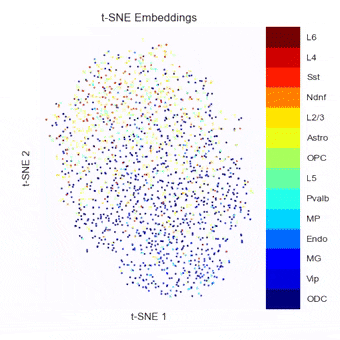
To address this, we have been developing a Python package which allows for easy embedding, clustering, and visualization of scHi-C data. In addition to implementing existing methods, we highlight the need to consider many different aspects of the data beyond just the embedding method, but including the resolution, preprocessing steps, and maximum/minimum distances considered.
While the package is still under development and not public quite yet, you can read the documentation here to see the package in action and some of the interesting use-cases.
